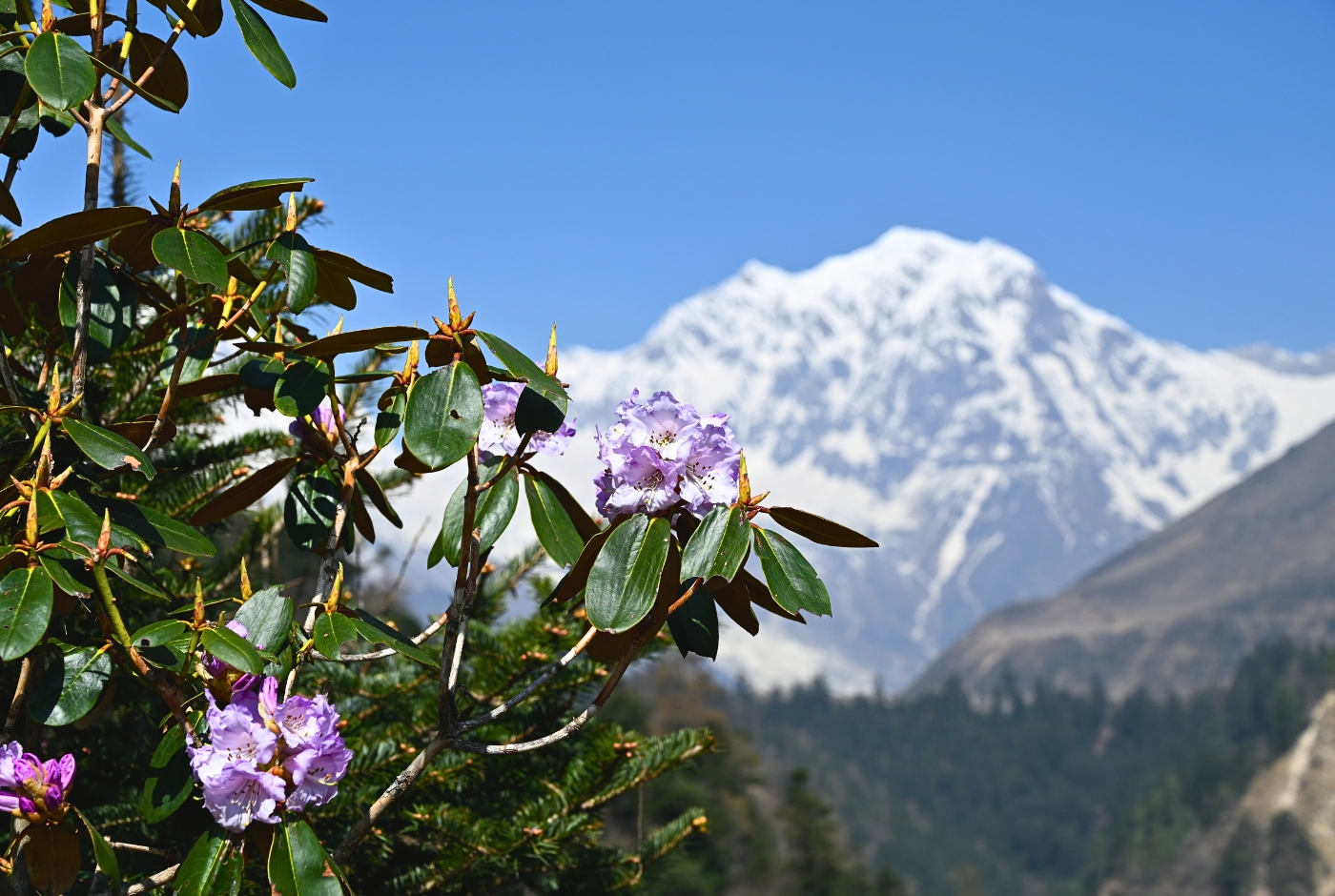
Once known as Shangri La, a hidden kingdom in the Himalayas, Nepal has emerged as one of the chief adventure destinations in the world. If you are a mountain person you will surely have visited or heard about Nepal. It is the country of the great mountains and brave Gurkha warriors.
A tiny landlocked country in South Asia, Nepal is home to some of the highest mountains, including Mount Everest (the highest of them all), on our planet. The country’s trekking trails weaving past some of the highest mountains in the world are some of the best walking and hiking destinations in the world. Each year, hundreds of mountaineers visit Nepal to scale its many mountains, ranging from over 5000 meters to 8000 meters.
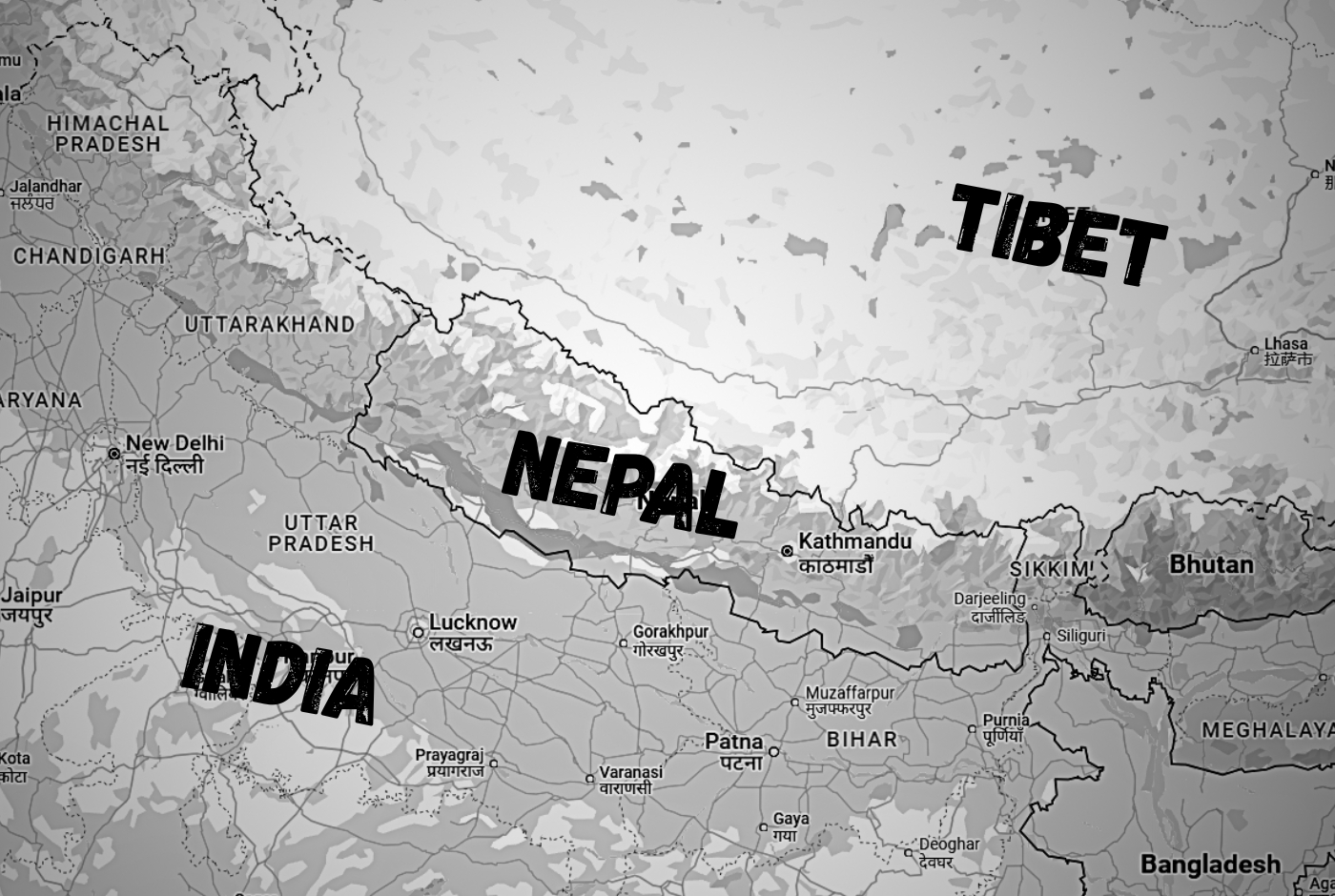
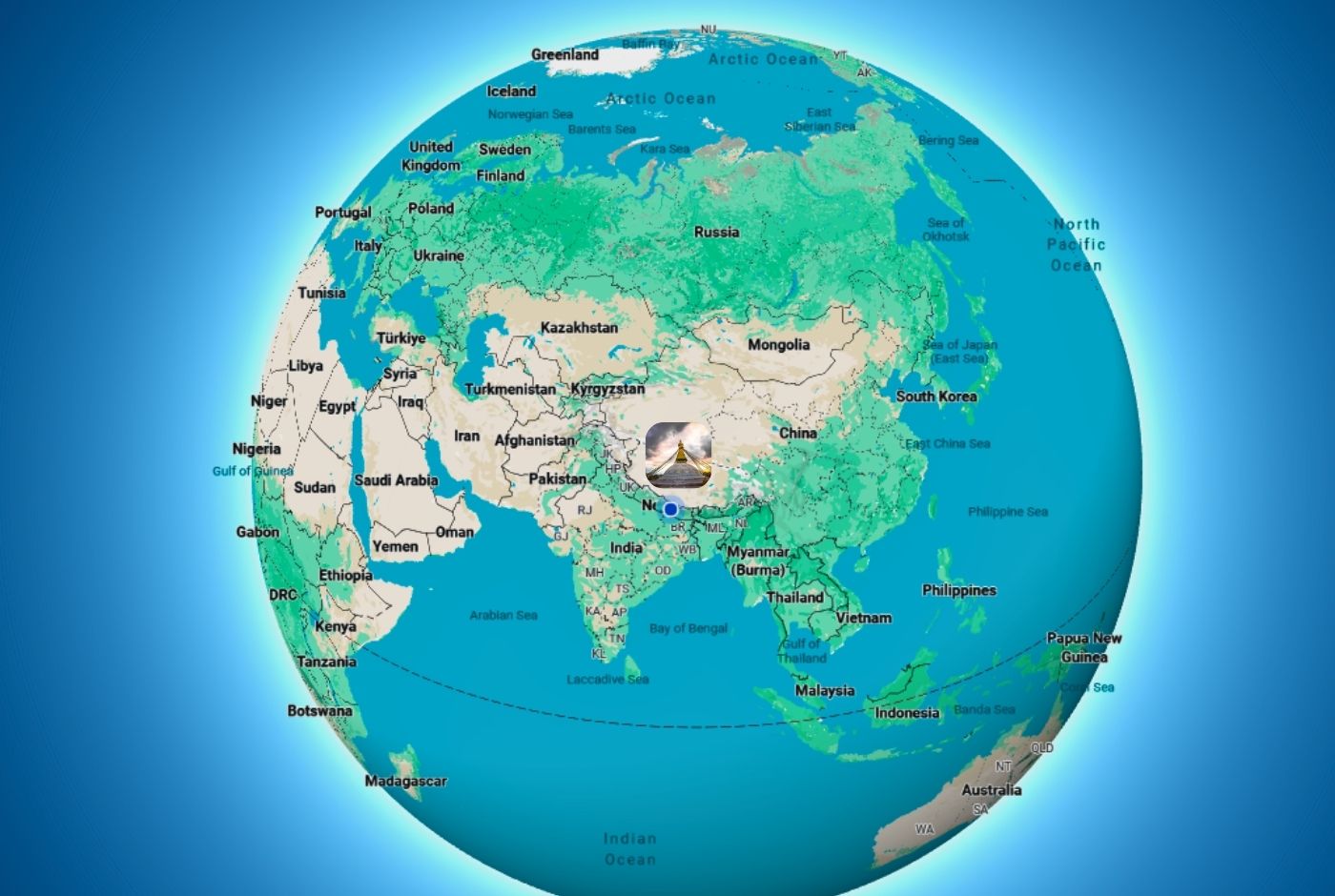
Nepal is a landlocked country located in South Asia, nestled in the Himalayan Mountains between China to the north and India to the south, east, and west. It is situated between the latitudes of approximately 26.22°N and 30.27°N and longitudes of 80.4°E and 88.12°E. It's not in China or in India either.
The big question; was Nepal ever part of China or India?
No, Nepal was never part of China or India; it has always been a separate, independent, sovereign nation, acting as a buffer state between the two giant neighbors, though it shares deep historical, cultural, and economic ties with both, particularly India. While Nepal faced British influence and treaties with India after losing territory in the Anglo-Nepalese War, it maintained its independence, unlike many other South Asian states.
But there’s more to Nepal than the mountains. The country has a rich cultural heritage that dates back to the time of Lord Buddha and earlier. The art and architecture found in Kathmandu Valley is one among the finest in the world.

Nepal is not Part of India and China (Tibet). Nepal is a separate, strong, and independent country
Is Nepal in India? Was it part of India?
No, Nepal is not in India. Nepal is a separate, independent country located in South Asia, bordering India to the south, east, and west. It is also bordered by China to the north. Kathmandu is the capital and largest city of Nepal. It is a landlocked country, meaning it has no direct access to the sea.
No, Nepal was never part of India. It has always been an independent nation, albeit with a complex relationship with the British Raj and later India. Nepal was never a princely state under British India, and it also never became part of the Dominion of India.
Nepal is Where? Where is Nepal in which country?
Is Nepal in Tibet or China? Was Nepal part of China?
Nepal is not in Tibet or China. Nepal is a separate, independent country located in South Asia, bordering China's Tibet Autonomous Region to the north, and India to the south, east, and west.
No, Nepal was never part of China. While Nepal has historically had close ties with China and has served as a buffer state between Imperial China and British India, it has always been an independent nation. Nepal maintains its own sovereignty and has a distinct political and cultural identity.
Neighboring Countries
Nepal’s immediate neighbors are India and China. It shares its east-west and south borders with India and its northern border with Tibet Autonomous Region of China. Bhutan also lies close to Nepal. Nepal is part of the SAARC nations. The citizens of SAARC nations enjoy special privileges while visiting Nepal.
Where is Nepal on the world map? Is it near China or India? Is Nepal Chinese or Indian?
Interesting Trivia about Nepal
Nepal does not have an ‘Independence Day’ as it has never been colonized by a foreign power. While its immediate neighbors India and China became the colonies of western powers like Great Britain, France, Portugal and the Netherlands, Nepal, protected by the high Himalayan mountains remained out of bounds from western influence or invasion.
Though the Anglo-Nepalese War was fought between the soldiers of the Gurkha dynasty and the British East India Company, the Britishers never got the chance to colonize Nepal like India. The Nepalese armies put up a good fight but lost. After the war, some of the Nepalese territories were ceded to the East India Company, but Nepal as a whole remained under the native rulers.
History of Nepal
According to popular legend, the Gopala dynasty was the first ruling dynasty in Nepal. The last king of this dynasty was Yaksha Gupta. After his death, the Mahispalas or Abhiras took over the reins of their kingdom. The rule of the Abhiras ended when Yalamber, the first Kirat king defeated the Abhira king in a battle and laid claim over their territory.
As per the Gopalavamsa chronicle, the first recorded rulers of Nepal were the Kiratas. Their kingdom stretched from the Kathmandu Valley to Teesta in the west and Tisida in the west. The Kirati dynasty had 29 kings and their reign lasted for 1225 years (800-300 BCE).
Yalamber, the greatest of the Kirati kings also finds a mention in the great Hindu epic ‘Mahabharata’. The Newars of Patan also call Patan as ‘Yala’ in remembrance of the Kirati king.
Lord Buddha is believed to have visited Kathmandu Valley during the reign of the 7th Kirati king Jitedasti. The rule of the Kiratas ended with King Gashti who was overthrown by the Somavanshi ruler Nimisha.
The Lichhavi era heralded the golden age in the history of Nepal. The kings of this era were connoisseurs of art and culture. Literature, art, architecture and a new social structure took shape and flourished during their reign. The oldest written inscription discovered in Nepal (at Changu Narayan Temple) dating back to 464 AD belongs to this era.
The Lichhavi kings maintained cordial relationships with the rulers of India and Tibet and there was an exchange of trade and ideas between them. Bhaskarvarma, Haridutta, Jayadeva, Vasudatta Varma, Manadeva I and II, Basantadeva, Shankerdeva and Gunakamadeva were some of the prominent rulers of this dynasty.
With the end of the Lichhavi dynasty the Thakuri kings assumed power. Amshuvarman who was a feudal lord laid the foundation of this dynasty. The Thakuri dynasty soon gave way to the powerful Malla dynasty.
Malla rule started with the reign of Ari Malla in the 12th century. Their reign lasted for 600 years (from the 12th century to the 18th century). Malla kings brought revolutionary changes in the socio-cultural and religious fabric of Nepal. Social and economic reforms took place, and a new form of art and architecture was introduced in the Kathmandu Valley.
Many of the UNESCO World Heritage Sites found in Kathmandu Valley belongs to the Malla era. Araniko, the master builder and craftsman who adorned the court of Kublai Khan was sent to China by Abhaya Malla. Jayasthiti Malla, Abhaya Malla, Yaksha Malla and Jaya Prakash Malla were some of the important Malla rulers. The Malla kingdom collapsed after the advent of the Gorkha King Prithvi Narayan Shah in Kathmandu Valley.
Prithvi Narayan Shah of the Gorkha dynasty is remembered for unifying Nepal and giving the country its present shape. Before his rule, Nepal was divided into several small kingdoms and principalities.
To expand his kingdom Prithvi Narayan Shah started his annexation campaign from Gorkha and moved towards the Kathmandu Valley that was under the Malla kings. After defeating them, he moved his capital from Gorkha to Kathmandu in 1768.
The Shah Kings expanded their kingdom from Teesta in the east to River Sutlej in Punjab and the Kumaon Hills which lies presently in India. Though the Shah dynasty remained in power till Nepal became a federal democratic republic in 2008, they were reduced to mere figureheads during the Rana regime.
The reign of the Ranas started with Jung Bahadur Rana who declared himself as the Prime Minister and placed his sons and nephews in the highest offices after the Kot Massacre. The kings of the Shah dynasty became mere figureheads under the Rana rule.
The Ranas appointed themselves as Regents of the Shah Kings and usurped the whole power of running the nation. Rana Prime Ministers ruled over Nepal from 1846 to 1953. After 1953 a popular movement against the oligarchic rule ousted the Ranas and King Tribhuvan Bir Bikram Shah was again hailed as the ruler of Nepal.
Panchyati Raj a kind of democratic set up was introduced and the first democratic elections were held in the country in 1959. But the parliamentary democracy was declared a failure and King Mahendra seized power again in 1960.
Monarchy in the country was finally abolished in Nepal after a decade long civil war ended with the Communist Party of Nepal gaining power. Declared a federal democratic republic in 2008, now Nepal’s government is chosen by the people
What is the capital of Nepal?
Kathmandu is the capital of Nepal, situated in the Kathmandu Valley in central Nepal at an altitude of 1,400 meters (4,600 feet). Historically, the Kathmandu Valley was known as "Nepal Mandala" and has been home to the Newar people for centuries. A brief history indicates Kathmandu was the royal capital of the Kingdom of Nepal and later became the seat of government for the Nepalese republic.
Where is Kathmandu, Napal?

What is the Language of Nepal?
The primary and official language of Nepal is Nepali, also known as Nepali or Hindi. While Nepali is widely spoken, Nepal also boasts a rich linguistic diversity with many other languages being spoken as mother tongues, including Maithili, Bhojpuri, Tamang, Tharu, Newari, and more.
Nepali: The Official Language
Nepali is an Indo-Aryan language and serves as the official language for administrative purposes, education, and communication. It is spoken by a significant portion of the population, making it a lingua franca across the country. Nepali is the language most often used in schools and for official business. It is written using the Devanagari script.
Other Languages Spoken in Nepal:
- Maithili: The second most spoken language in Nepal, Maithili is a relatively ancient language with a strong cultural identity.
- Bhojpuri: Another significant language in the Terai region, Bhojpuri is also spoken in neighboring parts of India.
- Tamang: A language belonging to the Tibeto-Burman language family, Tamang is spoken by the Tamang ethnic group, particularly in the Annapurna region.
- Tharu: Primarily spoken in the Terai region, Tharu is also spoken in nearby parts of India.
- Newari: Historically the language of the Kathmandu Valley, Newar is still spoken by a large community.

Other languages: Nepal has a wide array of other languages, reflecting the diverse ethnic groups within the country.
Flag of Nepal - Nepal flag Colors
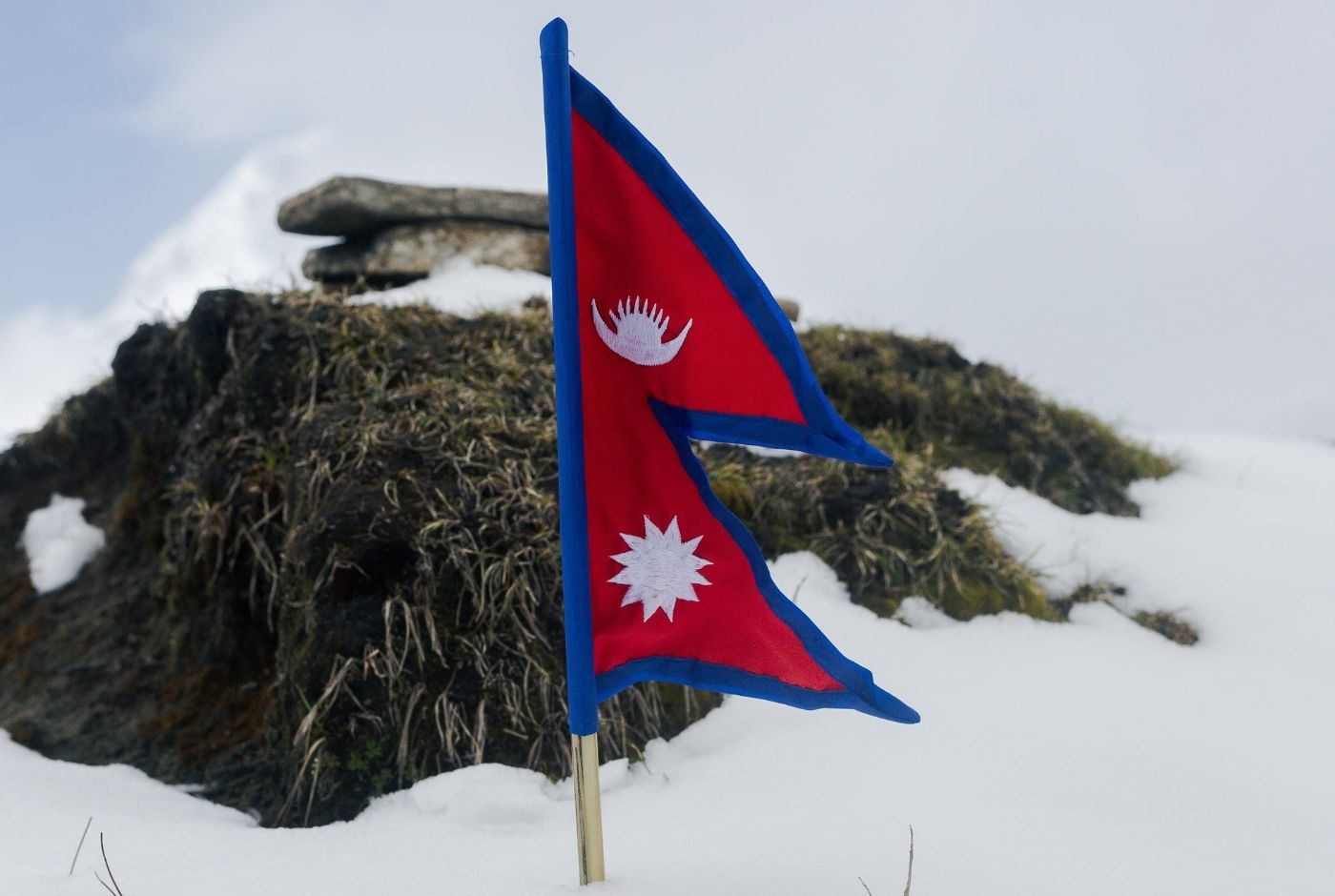

Is it Nepal or Napal? - The answer is Nepal
The country is officially known as Nepal (Federation Democratic Republic of Nepal) in English, and it is the correct name to use when referring to the nation.
Nepal Provision: How many states are in Nepal?
Nepal is divided into 7 provinces or states. These provinces are: Bagmati, Gandaki, Karnali, Koshi, Lumbini, Madhesh, and Sudurpashchim. The provinces replaced the previous administrative divisions of Development Regions, Administrative Zones, and Districts.
Here's a more detailed look at the provinces:
- Koshi Province: Located in the eastern part of Nepal, with its capital in Biratnagar.
- Madhesh Province: Situated in the southern plains of Nepal, known for its diverse ethnic and cultural makeup, with its capital in Birgunj.
- Bagmati Province: The most populated province, including the capital city of Kathmandu, with its capital in Kathmandu.
- Gandaki Province: A province in the western region, known for its stunning landscapes and mountain scenery, with its capital in Pokhara.
- Lumbini Province: Located in the central region, including the birthplace of Buddha, Lumbini, with its capital in Butwal.
- Karnali Province: Situated in the western part of Nepal, known for its mountainous terrain and remote areas, with its capital in Birendranagar.
- Sudurpashchim Province: Located in the far western part of Nepal, with its capital in Godawari.
How to get a Nepalese Visa?
If you are traveling to Nepal, you can get a visa on arrival. The process is completely hassle-free and takes only a couple of minutes, provided you have the right documents with you. You need to fill up your visa application form and provide your personal details together with a local contact address. The documents needed for the visa are:
Passport with 6 months validity. A recent passport-sized photograph with a light background
Keep some currency (USD preferably) handy to pay the Visa fee. To learn more about the visa fees and other visa formalities please visit the official site of Nepal’s Immigration Department.
Nationals of Nigeria, Afghanistan, Iraq, Somalia, Zimbabwe, Swaziland, Ghana, Liberia, Ethiopia, Palestine, Cameroon, Syria and refugees with travel documents are not eligible for visa on arrival. They have to obtain their visa from the embassy or consulate of the Nepal government in their country of residence before their arrival.
How to reach Nepal by air?
Nepal has one international airport, Tribhuvan International Airport. Three more international airports – Pokhara Regional International Airport, Gautam Buddha International Airport and Nijgadh International Airport – are under construction. At the time of writing this article (September 2020), the international airports at Pokhara and Bhairahwa were nearing completion and were about to come into operation.

One can fly into Nepal from Bangladesh, Bhutan, Singapore, Hong Kong, Turkey, Malaysia, South Korea, Japan, Oman, Qatar, Kuwait, Thailand, United Arab Emirates, India, Saudi Arabia and China. There are no direct flights from Europe, North America, Australia, South America, Africa and Australia, and one has to make a stopover at some of the aforementioned countries if one wants to fly into Nepal from these continents.
How to reach Nepal by land?
One can enter Nepal through India and China. The border entry points open for foreigners are Kakarbhitta, Pashupatinagar, Sunauli, Birganj, Belahia, Jamunaha, Mohana, Gaddichaukki, Kodari and Kerung.
Passport to travel to Nepal
To enter Nepal, most nationalities require a valid passport with at least six months of validity remaining beyond their intended stay. Additionally, a visa is generally needed, but Indian citizens are exempt and can enter Nepal with a valid passport or a voter card. Your passport must be valid for at least six months from your intended entry date into Nepal. Ensure your passport has at least two blank pages available for visa stamping.
A passport for Indian citizens to travel Nepal
Yes, a passport is required for travel to Nepal, but Indian citizens can also use a valid Voter ID issued by the Election Commission of India. While a passport is the preferred and most recommended document, a valid Voter ID is also accepted for Indian citizens entering Nepal by air or land.
Elaboration:
Indian Nationals: Indian citizens can travel to Nepal by air or land without a visa, but they need to carry either a valid passport or a valid Voter ID issued by the Election Commission of India.
Other Nationals: For other nationalities, a passport is required, and a visa is often needed.
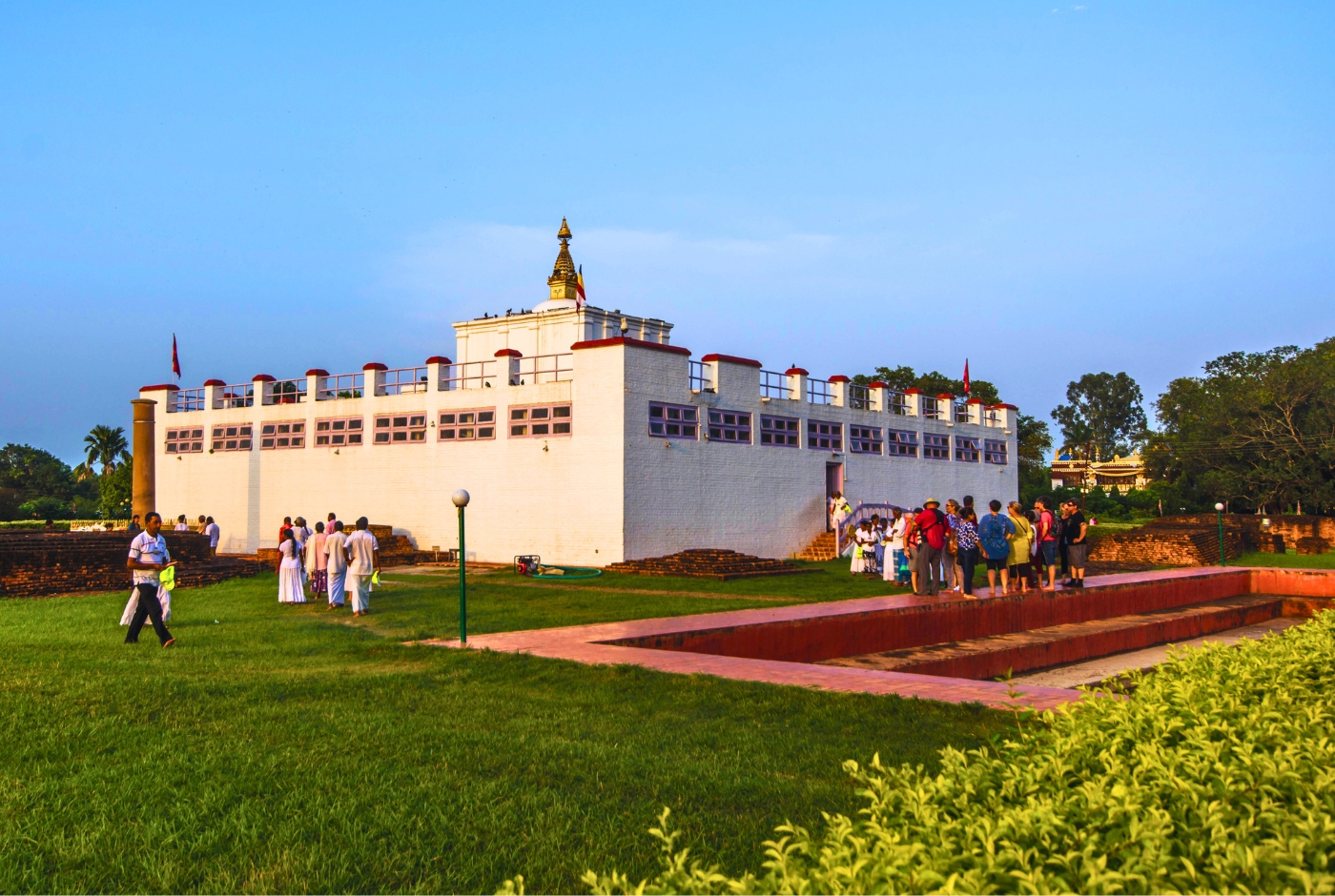
Where was Lord Buddha Born? Nepal or India
Lord Buddha was born in Lumbini, which is located in what is now Nepal. Lumbini is a sacred site and a UNESCO World Heritage site, and it's considered the birthplace of Siddhartha Gautama, the Buddha. While Siddhartha Gautama was born in the area that is now Nepal, the countries of Nepal and India as we know them today did not exist at the time.
Buddha was born in Nepal, not in India
Where is Napal?

What are the top treks in Nepal?
Some of the top treks in Nepal include the Annapurna Circuit, Everest Base Camp, Upper Mustang, and Manaslu Circuit.
Annapurna Circuit: A classic trek that circles the Annapurna range and Kali Gandaki River Valley. Includes crossing Thorong La Pass, the highest mountain pass in the Annapurna region
Offers views of Annapurna, Gangapurna, Machhapuchhre, Dhaulagiri, and Manaslu.
Everest Base Camp : A 14-day trek that starts in Kathmandu and ends at the base of Mount Everest. Follows the path of Sir Edmund Hillary and Tenjin Norgay Sherpa's 1953 Everest summit.
Upper Mustang: A trek that offers views of towering peaks and rugged ridges. Features the ethnic groups and landscape of the Upper Mustang region. Includes traditional Tibetan Buddhist practices
Manaslu Circuit: A 15-day trek.
Other top treks
- Annapurna Base Camp Trek
- Everest High Passes Trek
- Kanchenjunga Trek
- Everest Gokyo Lake Trek
- Pikey Peak Trek
- Langtang Gosaikunda Trek
- Khopra Ridge Trek
Nepal – Your next travel destination?
Beautiful, budget-friendly, and with a mind-boggling range of activities on offer, Nepal is the perfect holiday destination. The government and the people are tourist-friendly and travelers can expect a safe trip. Nepal is one of the safest destinations for solo female travelers. It is also the perfect destination for family vacations and MICE tours.
As the tourism industry is one of the biggest revenue earners in Nepal, the government together with private stakeholders have been developing the tourism infrastructure and introducing better policies to lure visitors to the country. Nepal also has a vast army of well-trained service providers and guides.
To provide safety and security to tourists visiting Nepal a special unit in the police force known as the ‘Tourist Police’ has been specially created. They are stationed at the major tourist hubs in the cities and towns ever ready to aid tourists in need of help.
Nepal has a range of accommodation options. From high-end luxury five star hotels to budget-friendly hostels, it’s not difficult to find your choice of accommodation. Moreover, Air B&B rentals and homestays allow you to live in local homes and experience the local lifestyle.
Incredible sights, inspiring nature, warm hospitality and nice locals, Nepal is the ultimate holiday destination. If you haven’t visited this Himalayan country, it’s high time you think about spending your next vacation in this gem of a country.



Post a Comment